Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Jinno, Satoshi; Fujita, Natsuko; Tanuma, Hajime*
Dai-23-Kai AMS Shimpojiumu Hokokushu, p.89 - 92, 2022/12
The measurement of chlorine-36 ( Cl) in AMS, which is important for the dating of saline groundwater, is more difficult than other nuclides due to the isobaric interference by sulfur-36 (
Cl) in AMS, which is important for the dating of saline groundwater, is more difficult than other nuclides due to the isobaric interference by sulfur-36 ( S). In general, acceleration voltages of 6 MV or higher are required to separate
S). In general, acceleration voltages of 6 MV or higher are required to separate  Cl and
Cl and  S. Therefore, this study aims to develop an ion funnel reaction cell and incorporate it into the low energy side of JAEA-AMS-TONO-5MV to selectively suppress
S. Therefore, this study aims to develop an ion funnel reaction cell and incorporate it into the low energy side of JAEA-AMS-TONO-5MV to selectively suppress  S.
S.
Shinto, Katsuhiro
Kasokuki, 14(4), p.248 - 250, 2018/01
The 17th International Conference on Ion Sources (ICIS 2017) was held on 15th - 20th October 2017 at Geneva in Switzerland. This conference is held biennially. Most of scientists and engineers for ion sources in the world meet at the conference in order to share results of research and development.
Shibata, Takanori*; Asano, Hiroyuki; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Naito, Fujio*; Nammo, Kesao*; Oguri, Hidetomo; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Takagi, Akira*; Ueno, Akira
AIP Conference Proceedings 1869, p.030017_1 - 030017_11, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:85.09(Physics, Applied)From September 2014, operation of Cs-seeded, multi-cusp, Radio Frequency (RF), hydrogen negative ion source (J-PARC source) has been started. The operation for 1,000 hours of J-PARC source has been achieved with H beam current 45 mA and duty factor of 1.25 % (0.5 msec and 25 Hz). In the present study, mechanisms of hydrogen plasma ramp-up and H
beam current 45 mA and duty factor of 1.25 % (0.5 msec and 25 Hz). In the present study, mechanisms of hydrogen plasma ramp-up and H production/transport processes in the steady state (which lasts for few 100 us) are investigated by numerical modeling for RF plasma. In the simulation, charged particle (e, H
production/transport processes in the steady state (which lasts for few 100 us) are investigated by numerical modeling for RF plasma. In the simulation, charged particle (e, H , H
, H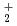 , and Cs
, and Cs ) transport, time variations of inductive and capacitive electromagnetic field, collision processes between charged and neutral (H, H
) transport, time variations of inductive and capacitive electromagnetic field, collision processes between charged and neutral (H, H ) particles are solved simultaneously. The model is applied to KEK parallel computation System-A with 32 nodes and 256 GB memory in order to solve high density RF plasma up to around 10
) particles are solved simultaneously. The model is applied to KEK parallel computation System-A with 32 nodes and 256 GB memory in order to solve high density RF plasma up to around 10 m
m with adequate statisticity. In the presentation, time variations of plasma density distributions and average energy are shown with electromagnetic field variations.
with adequate statisticity. In the presentation, time variations of plasma density distributions and average energy are shown with electromagnetic field variations.
Hanada, Masaya; Kojima, Atsushi; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Nishikiori, Ryo; Hiratsuka, Junichi; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Umeda, Naotaka; Yoshida, Masafumi; Ichikawa, Masahiro; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 87(2), p.02B322_1 - 02B322_4, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:49.05(Instruments & Instrumentation)In International Thermo-nuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) and JT-60 Super Advanced (JT-60 SA), the D ion beams of 1 MeV, 40 A and 0.5 MeV, 22 A are required to produce 3600 s and 100 s for the neutral beam injection, respectively. In order to realize such as powerful D
ion beams of 1 MeV, 40 A and 0.5 MeV, 22 A are required to produce 3600 s and 100 s for the neutral beam injection, respectively. In order to realize such as powerful D ion beams for long duration time, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has energetically developed cesium (Cs)-seeded negative ion sources (CsNIS) and electro-static multi-aperture and multi-stage accelerators (MAMuG accelerator) which are chosen as the reference design of ITER and JT-60 SA. In the development of the CsNIS, a 100s production of the H
ion beams for long duration time, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has energetically developed cesium (Cs)-seeded negative ion sources (CsNIS) and electro-static multi-aperture and multi-stage accelerators (MAMuG accelerator) which are chosen as the reference design of ITER and JT-60 SA. In the development of the CsNIS, a 100s production of the H ion beam has been demonstrated with a beam current of 15 A by modifying the JT-60 negative ion source. At the higher current, the long pulse production of the negative ions has been tried by the mitigation of the arcing in the plasma inside the ion source. As for the long pulse acceleration of the negative ions in the MAMuG accelerator, the beam steering angle has been controlled to reduce the power loading of the acceleration grids A pulse duration time has been significantly extended from 0.4 s to 60 s at reasonable beam power for ITER requirement. The achieved pulse duration time is limited by the capacity of the power supplies in the test stand. In the range of
ion beam has been demonstrated with a beam current of 15 A by modifying the JT-60 negative ion source. At the higher current, the long pulse production of the negative ions has been tried by the mitigation of the arcing in the plasma inside the ion source. As for the long pulse acceleration of the negative ions in the MAMuG accelerator, the beam steering angle has been controlled to reduce the power loading of the acceleration grids A pulse duration time has been significantly extended from 0.4 s to 60 s at reasonable beam power for ITER requirement. The achieved pulse duration time is limited by the capacity of the power supplies in the test stand. In the range of  60 s, there are no degradations of beam optics and voltage holding capability in the accelerator. It leads to the further extension of the pulse duration time at higher power density. This paper reports the latest results of development on the negative ion source and accelerator at JAEA.
60 s, there are no degradations of beam optics and voltage holding capability in the accelerator. It leads to the further extension of the pulse duration time at higher power density. This paper reports the latest results of development on the negative ion source and accelerator at JAEA.
Chiba, Atsuya; Usui, Aya; Yamada, Keisuke
Dai-28-Kai Tandemu Kasokuki Oyobi Sono Shuhen Gijutsu No Kenkyukai Hokokushu, p.53 - 56, 2015/12
no abstracts in English
Kojima, Atsushi; Umeda, Naotaka; Hanada, Masaya; Yoshida, Masafumi; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Akino, Noboru; Komata, Masao; Mogaki, Kazuhiko; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 55(6), p.063006_1 - 063006_9, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:89.45(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Significant progresses in the extension of pulse durations of powerful negative ion beams have been made to realize the neutral beam injectors for JT-60SA and ITER. In order to overcome common issues of the long pulse production/acceleration of negative ion beams in JT-60SA and ITER, the new technologies have been developed in the JT-60SA ion source and the MeV accelerator in Japan Atomic Energy Agency. As for the long pulse production of high-current negative ions for JT-60SA ion source, the pulse durations have been successfully increased from 30 s at 13 A on JT-60U to 100 s at 15 A by modifying the JT-60SA ion source, which satisfies the required pulse duration of 100 s and 70% of the rated beam current for JT-60SA. This progress was based on the R&D efforts for the temperature control of the plasma grid and uniform negative ion productions with the modified tent-shaped filter field configuration. Moreover, the each parameter of the required beam energy, current and pulse has been achieved individually by these R&D efforts. The developed techniques are useful to design the ITER ion source because the sustainment of the cesium coverage in large extraction area is one of the common issues between JT-60SA and ITER. As for the long pulse acceleration of high power density beams in the MeV accelerator for ITER, the pulse duration of MeV-class negative ion beams has been extended by more than 2 orders of magnitude by modifying the extraction grid with a high cooling capability and a high-transmission of negative ions. A long pulse acceleration of 60 s has been achieved at 70 MW/m (683 keV, 100 A/m
(683 keV, 100 A/m ) which has reached to the power density of JT-60SA level of 65 MW/m
) which has reached to the power density of JT-60SA level of 65 MW/m .
.
Kojima, Atsushi; Hanada, Masaya; Yoshida, Masafumi; Umeda, Naotaka; Hiratsuka, Junichi; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Grisham, L. R.*; NB Heating Technology Group
AIP Conference Proceedings 1655, p.060002_1 - 060002_10, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:87.25(Physics, Applied)In this paper, the recent activities on the new test stand are reported toward demonstration of the long pulse production for 22A, 100s negative ion beams. As for the temperature control of the plasma grid, a prototype of the grid with cooling/heating by circulating a high-temperature fluorinated fluid has been improved to cover the full extraction area by using 5 segments of the PG. These grids were found to have a capability to control the temperature with a time constant of 10s as well as the prototype grid. As a result, 15A negative ion beams for 100s have been achieved.
 ion beam for ITER
ion beam for ITERUmeda, Naotaka; Kojima, Atsushi; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Hiratsuka, Junichi; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Dairaku, Masayuki; Yamanaka, Haruhiko; Hanada, Masaya
AIP Conference Proceedings 1655, p.050001_1 - 050001_10, 2015/04
For ITER neutral beam system, negative deuterium ion beam of 1 MeV, 40 A (current density of 200 A/m ) is required for 3600 s. To demonstrate ITER relevant negative ion beam acceleration, beam acceleration test has been carried out at MeV test facility in JAEA. The present target is H
) is required for 3600 s. To demonstrate ITER relevant negative ion beam acceleration, beam acceleration test has been carried out at MeV test facility in JAEA. The present target is H ion beam acceleration up to 1 MeV with 200 A/m
ion beam acceleration up to 1 MeV with 200 A/m for 60 s, which beam energy and pulse length are the present facility limit. To extend pulse duration time up to facility limit at high power density beam, new extraction grid has been developed with high cooling capability, which electron suppression magnet is placed under cooling channel. In addition, the aperture size of the electron suppression grid is enlarged from 14 mm to 16 mm and the aperture displacement is modified to reduce collision of negative ion beam on the grid. By these modifications, total grid power loading has reduced from 14% to 11%. As a result, beam acceleration up to 60 s which is the facility limit, has achieved at 700 kV, 100 A/m
for 60 s, which beam energy and pulse length are the present facility limit. To extend pulse duration time up to facility limit at high power density beam, new extraction grid has been developed with high cooling capability, which electron suppression magnet is placed under cooling channel. In addition, the aperture size of the electron suppression grid is enlarged from 14 mm to 16 mm and the aperture displacement is modified to reduce collision of negative ion beam on the grid. By these modifications, total grid power loading has reduced from 14% to 11%. As a result, beam acceleration up to 60 s which is the facility limit, has achieved at 700 kV, 100 A/m of negative ion beam without breakdown.
of negative ion beam without breakdown.
Chiba, Atsuya; Usui, Aya; Yamada, Keisuke
Dai-27-Kai Tandemu Kasokuki Oyobi Sono Shuhen Gijutsu No Kenkyukai Hokokushu, p.56 - 59, 2015/03
Utilization of the swift fullerene ion beam in TIARA using the tandem accelerator tends to increase year after year. However, only a few currents obtained by a generating method of negative ions with a cesium sputtering is hindrance to the progress of study. A generating method of the negative fullerene ions is developed on the basis of an electron attachment. As a result, the method permits us to obtain stable beam intensity more than a thousand-fold compared with that produced by the sputtering method.
Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Umeda, Naotaka; Akino, Noboru; Ebisawa, Noboru; Grisham, L. R.*; Hanada, Masaya; Honda, Atsushi; Inoue, Takashi; Kawai, Mikito; Kazawa, Minoru; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 46(6), p.S211 - S219, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:59 Percentile:87.2(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Recently, the extension of the pulse duration up to 30 sec has been intended to study quasi-steady state plasma on JT-60U N-NBI system. The most serious issue is to reduce the heat load on the grids for long pulse operation. Two modifications have been proposed to reduce the heat load. One is to suppress the beam spread which may be caused by beamlet-beamlet interaction in the multi-aperture grid due to the space charge force. Thin plates were attached on the extraction grid to modify the local electric field. The plate thickness was optimized to steer the beamlet deflection. The other is to reduce the stripping loss, where the electron of the negative ion beam is stripped and accelerated in the ion source and then collides with the grids. The ion source was modified to reduce the pressure in the accelerator column to suppress the beam-ion stripping loss. Up to now, long pulse injection of 17 sec for 1.6 MW and 25 sec for  1 MW has been obtained by one ion source with these modifications.
1 MW has been obtained by one ion source with these modifications.
Umeda, Naotaka; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Hanada, Masaya; Inoue, Takashi; Kawai, Mikito; Kazawa, Minoru; Komata, Masao; Mogaki, Kazuhiko; Oga, Tokumichi
Review of Scientific Instruments, 77(3), p.03A529_1 - 03A529_3, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:34.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
 -ion source for the High-Intensity Proton Accelerator (J-PARC)
-ion source for the High-Intensity Proton Accelerator (J-PARC)Oguri, Hidetomo; Ueno, Akira; Namekawa, Yuya*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*
Review of Scientific Instruments, 77(3, Part2), p.03A517_1 - 03A517_3, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:29.76(Instruments & Instrumentation)The J-PARC Project was started in 2001 as a joint project carried out by JAERI and KEK. At the first stage of the J-PARC, the linac will accelerate the H- ion beam current of 30 mA with a duty factor of 1.25 %. The J-PARC H- ion source driven with a LaB6 filament has regularly delivered more than 35 mA beam with a duty factor of 0.9 % without resorting to cesium. Although the operated duty factor is about 1/3 of the requirement, the filament is not replaced for a half year. At the J-PARC, the lifetime of the tungsten (W) filament was measured by using another H- ion source, which can produce a 72 mA with cesium seeded. The experimental results showed that there is a possibility of the W filament satisfying the lifetime of more than 500 hours, which is J-PARC requirement. We consider the W driven plasma ion source is one of the candidates for the J-PARC source. At present, we are performing the beam test of the cesium free ion source driven with W. We will present the experimental data of the beam test in this conference.
Umeda, Naotaka; Yamamoto, Takumi; Hanada, Masaya; Grisham, L. R.*; Kawai, Mikito; Oga, Tokumichi; Akino, Noboru; Inoue, Takashi; Kazawa, Minoru; Kikuchi, Katsumi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 74(1-4), p.385 - 390, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:53.19(Nuclear Science & Technology)In negative ion based neutral beam injector (N-NBI) for JT-60U, some modifications for extent pulse duration from 10 second, which is design value, to 30 second was conducted. Main limit to prevent pulse extension was heat loads onto grounded grid in an ion source and onto beam limiter placed at 22 m from the ion source. To reduce these heat loads, beam extraction area was optimized and the limiter was changed to one which had about twice thermal capacity. As a result of these modifications, the temperature rise of the water which was cooling grounded grid could be suppressed under 40 degree, which can operate in steady state condition. The temperature rise of the limiter could be restricted to 60%. Untill now the beam pulse extended to 17 second of 1.6MW power at 366keV energy, and injection of 30 seconds will be achieved in next experiment.
Okano, Kunihiko*; Suzuki, Takahiro; Umeda, Naotaka; Hiwatari, Ryoji*; Masaki, Kei; Tobita, Kenji; Fujita, Takaaki
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 81(8), p.579 - 580, 2005/08
In a toroidal system, circulating fast ions generated by neutral beam injection affect the beam stopping cross-section of the neutral beam itself. This effect is called "beam particle self-interaction (BPSI)". In a recent experiment in JT-60U with 350 keV H beam, an indication of this BPSI effect has been found for the first time. In a low density discharge at about 1
beam, an indication of this BPSI effect has been found for the first time. In a low density discharge at about 1 10
10 m
m , the beam shine-through decreased by about 35% within several hundred msec after beam injection. This result is consistent with a prediction by the BPSI theory.
, the beam shine-through decreased by about 35% within several hundred msec after beam injection. This result is consistent with a prediction by the BPSI theory.
 n eigenmodes driven by negative-ion-based neutral beams in JT-60U
n eigenmodes driven by negative-ion-based neutral beams in JT-60UShinohara, Koji; Ishikawa, Masao; Takechi, Manabu; Kusama, Yoshinori; Todo, Yasushi*; Gorelenkov, N. N.*; Cheng, C. Z.*; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Kramer, G.*; Nazikian, R. M.*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 81(7), p.547 - 552, 2005/07
In the bursting instabilities in the frequency range of Alfven Eigenmode, we observed two types of modes phenomenologically. In one type, the time scale of the mode was  1ms and the mode amplitude was so large that we were able to detect apparent enhanced transport of the energetic ions. The enhanced transport showed the clear energy dependence by using new diagnostics, natural diamond detector. In another type, the mode amplitude is not so large, compared with the first type. The frequency up-down chirping is clearly observed with the time-scale of a few ms. This frequency chirping was reproduced by the newly developed simulation code, MEGA To demonstrate this model of Reversed-Shear-induced Alfven Eigenmode, RSAE, we have performed experiments in the condition where we can have q profile with a good signal-to-noise ratio. We observed the slow up-frequency sweeping of RSAE due to the down evolution of qmin, We have analyzed this experiment by using NOVA-K code. We observed that the most unstable mode localized around qmin.
1ms and the mode amplitude was so large that we were able to detect apparent enhanced transport of the energetic ions. The enhanced transport showed the clear energy dependence by using new diagnostics, natural diamond detector. In another type, the mode amplitude is not so large, compared with the first type. The frequency up-down chirping is clearly observed with the time-scale of a few ms. This frequency chirping was reproduced by the newly developed simulation code, MEGA To demonstrate this model of Reversed-Shear-induced Alfven Eigenmode, RSAE, we have performed experiments in the condition where we can have q profile with a good signal-to-noise ratio. We observed the slow up-frequency sweeping of RSAE due to the down evolution of qmin, We have analyzed this experiment by using NOVA-K code. We observed that the most unstable mode localized around qmin.
Mogaki, Kazuhiko; Kawai, Mikito; Kazawa, Minoru; Komata, Masao; Umeda, Naotaka; Ikeda, Yoshitaka
Heisei-16-Nendo Osaka Daigaku Sogo Gijutsu Kenkyukai Hokokushu (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2005/03
no abstracts in English
Honda, Atsushi; Kawai, Mikito; Okano, Fuminori; Oshima, Katsumi*; Numazawa, Susumu*; Oga, Tokumichi; Ikeda, Yoshitaka
Heisei-16-Nendo Osaka Daigaku Sogo Gijutsu Kenkyukai Hokokushu (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2005/03
no abstracts in English
Kusama, Yoshinori; Ishikawa, Masao; Takechi, Manabu; Nishitani, Takeo; Morioka, Atsuhiko; Sasao, Mamiko*; Isobe, Mitsutaka*; Krasilnikov, A.*; Kaschuck, Y.*
Proceedings of Plasma Science Symposium 2005/22nd Symposium on Plasma Processing (PSS-2005/SPP-22), p.395 - 396, 2005/00
The energetic neutral particles have been successfully measured with a natural diamond detector in the neutron and  ray radiation circumstance of the JT-60U deuterium discharges. The diamond detector was covered with polyethylene and lead in order to reduce the neutron and
ray radiation circumstance of the JT-60U deuterium discharges. The diamond detector was covered with polyethylene and lead in order to reduce the neutron and  ray background. The shield has shown expected shielding capability. A rapid increase in neutral particles has been observed at the onset of the Toroidal Alfven Eigenmode (TAE) excited by the negative-ion-based neutral beam injection. The energy range of increased neutral particles has agreed well with that predicted from the resonant interaction between the energetic ions and the TAE.
ray background. The shield has shown expected shielding capability. A rapid increase in neutral particles has been observed at the onset of the Toroidal Alfven Eigenmode (TAE) excited by the negative-ion-based neutral beam injection. The energy range of increased neutral particles has agreed well with that predicted from the resonant interaction between the energetic ions and the TAE.
Sakurai, Shinji; JT-60 Team
Plasma Science and Technology, 6(1), p.2151 - 2158, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Yamamoto, Takumi; Oga, Tokumichi; Kawai, Mikito; Akino, Noboru; Kazawa, Minoru; Umeda, Naotaka
Heisei-16-Nen Denki Gakkai Zenkoku Taikai Koen Rombunshu, 219 Pages, 2004/00
In JAERI, 10 MW and 500 keV negative-ion based neutral beam injection (N-NBI) system for JT-60U was constructed in 1996, in order to study a plasma heating and current drive in high-density plasma by high-energy beam injection. Thereafter, improvement of beam performance has been carried out while N-NBI system was available for experiments on JT-60U. The maximum beam energy of 418 keV and the maximum injection power of 6.2 MW have been achieved with a hydrogen beam, so far. In addition, 10 seconds of injection pulse duration, which is the designed value, was attained at the injection power of 2.6MW. Further improvement is required for the performance to reach to the final targets. It was made it clear that the performance was limited by the withstanding voltage of acceleration and heat load on acceleration grids in the ion source.